Visibility
Feedback
Constraints
Mapping
Consistency
Affordances
VISIBILITY

This is a control panel for an elevator.
How does it work?
Push a button for the floor you want?
Nothing happens. Push any other button? Still nothing. What do you need to do?
It is not visible as to what to do!

…you need to insert your room card in the slot by the buttons to get the elevator to work!

How to make this action more visible?
make the card reader more obvious ?
provide an auditory message, that says what to do (which language?)
provide a big label next to the card reader that flashes when someone enters?
Other?
VISIBILITY
One of the most important design principles is visibility
Visibility is achieved by placing the controls in a
highly visible location
Designing for visibility means that just by looking, users
can see the possibilities for action
Visibility is often violated in order to make things
"look good"
FEEDBACK

Feedback is the provision of information to a user about the result of an action
When feedback is used in design, the system tells the user that it has done something in response to the user's input
CONSTRAINTS

Constraints are properties of an object that limit the ways in which it can be used
Jigsaws puzzle pieces utilise shape as well as the printed picture/pattern to provide constraints
When constraints are used in design, we reduce the possibility of users making errors
Three main types to represent constraints (Norman, 1999)
Physical
Logical
Cultural

a professor emeritus at University of California, San Diego, works mostly with cognitive science in the domain of usability engineering. Co-founded the Nielsen Norman Group, a consulting group on matters of usability which also includes Jakob Nielsen and Bruce Tognazzini.
CONSTRAINTS-PHYSICAL
The design of floppy disk drives allows the disk to be inserted in the correct way only
The design of video cassette drives allows the cassette to be inserted in the correct way only
Bank card can be inserted in certain way, keys on a pad can only be pressed in certain way. (ATM machine)
CONSTRAINTS-LOGICAL

Where do you plug the mouse and keyboard?
top or bottom connector?
trial and error? experience?
Do the colour coded
icons help?
Do you find them ambiguous? How to design them more logically?
How to design them more logically?

A provides direct adjacent mapping between icon and connector
B provides colour coding to associate the connectors with the labels
CONSTRAINTS-CULTURAL
How to represent Danger!??

Cultural constraints rely on learned conventions
(e.g. red for warning, certain audio signals for danger, smiley face for happy emotions)
Once accepted by more than one cultural groups, they become universally accepted conventions.
Which are universal and which are culturally-specific?

CONSTRAINTS
Restricting the possible actions that can be performed
Helps prevent user from selecting incorrect options
MAPPING

Why is this a poor mapping of control buttons for the sequence of actions of fast rewind, rewind, play and fast forward?
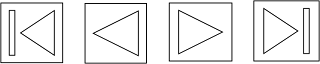
Why is this a better mapping?

NATURAL MAPPING
Mapping is the relationship between controls and their action or effect in the world
Natural mapping takes advantage of physical analogies and cultural standards to provide the user with an understanding of how something works
CONSISTENCY
Design interfaces to have similar operations and use similar elements for similar tasks
For example:
Use of short cut keys
always use ctrl key plus first initial of the command for an operation
– ctrl+C, ctrl+S, ctrl+O
Main benefit is consistent interfaces are easier to learn and use
When consistency breaks down?
What happens if there is more than one command starting with the same letter?
- e.g. save, spelling, select, style
Have to find other initials or combinations of keys, thereby breaking the consistency rule
- e.g. ctrl+S, ctrl+shift+L
Increases learning burden on user, making them more prone to errors
CONSISTENCY (INTERNAL AND EXTERNAL)
Internal consistency refers to designing operations to behave the same within an application
External consistency refers to designing operations, interfaces, etc., to be the same across applications (e.g. MS Office applications) and devices (calculators, remote controls, phone keypads, ATM keypads)
AFFORDANCES

This set of doors connects a walkway between two buildings
Although both sides of both sets of
doors have handles, only the outer
handles are meant to be pulled
Using either set of doors once inside
the walkway, to exit, one needs to
push
Feel trapped??
AFFORDANCES (PHYSICAL)
Physical affordances:
How do the following physical objects afford?
Are they obvious?

AFFORDANCES (LOGICAL)
Virtual affordances (logical)
How do the following screen objects afford?
What if you were a novice user?
Would you know what to do with them?

DESIGN PRINCIPLES REVISITED
Visibility
Placing the controls in a highly visible location
Feedback
provision of information about the result of an action
Constraints
Restricting the possible actions that can be performed helps prevent user from selecting incorrect options
Mapping
Mapping is the relationship between controls and their action or effect in the world
Consistency
Internal consistency refers to designing operations to behave the same within an application
External consistency refers to designing operations, interfaces, etc., to be the same across applications and devices
Affordances
properties of an object that indicate how it can be used
Wow... absolutely the same explanations and pictures presented in our class. I have this feeling that our professor copied it from here. Thanks a lot for all the information posted in your blog. :)
ReplyDeleteFantastic read, thanks a mil, this is exactly what i was looking for
ReplyDelete